The most frequent symptoms associated to allergic disorders are shown here in alphabetical order. You can check them by the organ involved with our Allergy Body Guide.
IMPORTANT TO NOTE: None of these symptoms are exclusive of allergy. Any of them can be caused by other conditions, some of them very serious. The symptoms are shown here for information, but if you suffer from them we recommend you to visit a doctor.
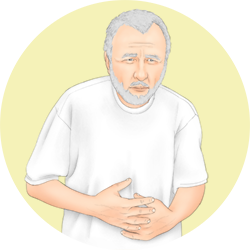
Abdominal pain
A pain in the stomach area, often associated to vomiting or diarrhoea, appears when the digestive system if not functioning correctly. When the pain is colicky it is due to the accelerated movement of the bowels trying to expel their contents as fast as possible. This is associated to allergic disorders such as food allergy, hereditary angioedema and anaphylaxis.

Chest tightness
Sensation of pressure on the chest, it causes difficulty in breathing. It appears when we try to expand our chest to let air come in. If the airways are narrowed and the air cannot pass easily you will feel this sensation. This is associated to allergic disorders such as asthma or anaphylaxis.

Cough
When we cough, we expel air from the lungs forcefully, which helps to clear the airways from secretions, irritants, and foreign particles such as allergens and microbes. This is associated to allergic disorders such as asthma, rhinitis, rhinosinusitis, hay fever and anaphylaxis.

Diarrhoea
Discharge of loose or liquid stools, when a food has not been digested, or due to an accelerated transit of the food in the bowels, to expel something that the organism does not admit. This is associated to allergic disorders such as food allergy and anaphylaxis.

Dyspnoea
The feeling of difficulty in inhaling or exhaling air appears when we try to breathe through a narrowed airway. It is a warning signal, and if not reverted, it can lead to exhaustion of the respiratory muscles. You can have this feeling if you try to breathe through a straw. This is associated to allergic disorders such as asthma and anaphylaxis.

Difficulty swallowing
A feeling of pain or discomfort when swallowing, or even the sensation that the food is stuck, can appear once the food passes through a constricted and rigid oesophagus, due to the infiltration of inflammatory cells. This is associated to allergic disorders such as eosinophilic esophagitis.

Dizziness
Dizziness means an impairment in spatial perception and stability. It can appear due to a drop in blood pressure – called shock – when it is extreme. This is associated to allergic disorders such as anaphylaxis.

Eye circles
The blood coming from the eyes and going to the heart passes through the veins in the nose. If these are congested due to inflammation of the nasal mucosa, eye circles appear. This is associated to allergic disorders such as rhinitis, hay fever, conjunctivitis and anaphylaxis.

Eye itchiness
Due to infiltration of cells in the nasal mucosa it is an alarm warning that something is going wrong in our eyes. This is associated to allergic disorders such as conjunctivitis and anaphylaxis.

Eye redness
Due to the dilation of blood vessels in the surface of the eyeballs, these appear red. This is associated to allergic disorders such as conjunctivitis and anaphylaxis.

Headache
Among many other causes, headache can occur due to nasal congestion or to the blockage of the mucus secretion in the sinuses – cavities within the bones of the head. This is associated to allergic disorders such as rhinitis, hay fever and rhinosinusitis.

Loss of smell
The loss of the sense of smell is due to a malfunctioning of the nose when there is an infiltration of the nasal mucosa or an abnormal growth of tissue, forming polyps. This is associated to allergic disorders such as rhinitis, hay fever and nasal polyposis.

Nasal blockage
The blocking of the passage of air through the nose can happen when there is an obstruction due to mucus secretion, to the inflammation of the nose, to the hypertrophy of the bones inside the nose called turbinates, or to the growth of tissue inside the nose, forming polyps. This is associated to allergic disorders such as rhinitis, hay fever, nasal polyposis and anaphylaxis.
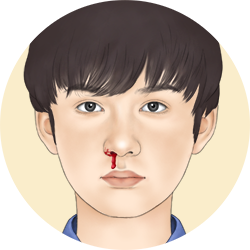
Nasal bleed
Bleeding from the nose can happen when the nasal mucosa is infiltrated and thus congested with blood vessels and very fragile. This is associated to allergic disorders such as rhinitis, hay fever and nasal polyposis.
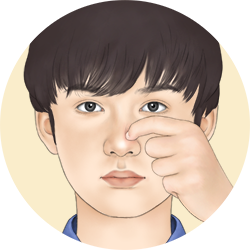
Nose itching
Due to infiltration of cells in the nasal mucosa it is an alarm warning that something is wrong in our nose. This is associated to allergic disorders such as rhinitis, hay fever and anaphylaxis.
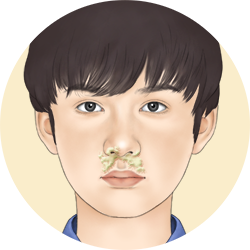
Nose mucus
Either liquid or thick, transparent or coloured, mucus in the nose has the objective of catching and neutralising stimuli identified as harmful. This is associated to allergic disorders such as rhinitis, hay fever and anaphylaxis.
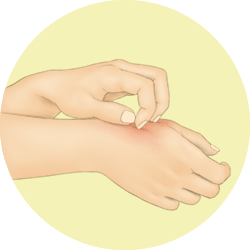
Skin itching
The sensation that causes the desire or reflex to scratch appears due to the stimulation of skin receptors and may act as a signal that something is wrong. This is associated to allergic disorders such as atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, urticaria and anaphylaxis
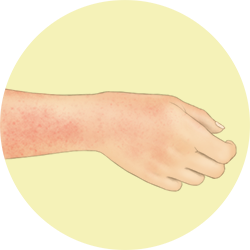
Skin redness
These appear when the blood vessels are dilated due to harmful stimuli, when the protecting fatty layer of the skin is not repaired, and when the normal cycle of renewal of the skin is impaired. These are associated to allergic disorders such as atopic dermatitis or contact dermatitis.

Sneezing
This sudden loud expulsion of air from the lungs through the nose and mouth helps clearing the airways from substances identified as harmful. This is associated to allergic disorders such as rhinitis, hay fever and anaphylaxis.
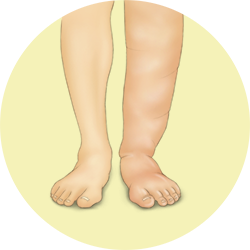
Skin inflammation
This is due to the drip of liquid from the blood vessels to the deeper layers of the skin. This is associated to allergic disorders such as urticaria, anaphylaxis and hereditary angioedema.

Swollen eyelids
They appear due to the drip of liquid from the blood vessels to the skin, due to a local congestion or to a generalised reaction. This is associated to allergic disorders such as rhinitis, hay fever, conjunctivitis, anaphylaxis and hereditary angioedema.

Swollen face
Swelling of the face appears due to the drip of liquid from the blood vessels to the skin, due to a local or a generalised reaction. This is associated to allergic disorders such as urticaria, anaphylaxis and hereditary angioedema.

Tearing
The secretion of tears helps clearing the eyes from foreign substances; at the same time some components in tears neutralise these substances. This is associated to allergic disorders such as conjunctivitis and anaphylaxis.

Vomiting
The involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one’s stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose has the objective of getting rid of content that the organism identifies as harmful. This is associated to allergic disorders such as food allergy and anaphylaxis.
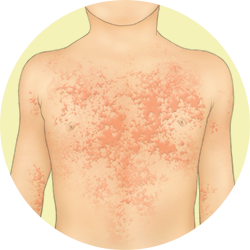
Weals or hives
They are pale red, raised, itchy bumps in the skin, due to the drip of liquid from the blood vessels to the superficial layers of the skin. They are associated to allergic disorders such as urticaria and anaphylaxis.

Wheeze
Wheezing is a whistling sound produced during breathing, when the air passes through a narrowed or obstructed airway. It can happen in bronchospasm, when bronchi contract trying to prevent the passage of harmful stimuli, but at the same time, this constriction impairs the passage of air. This is associated to allergic disorders such as asthma or anaphylaxis.
